



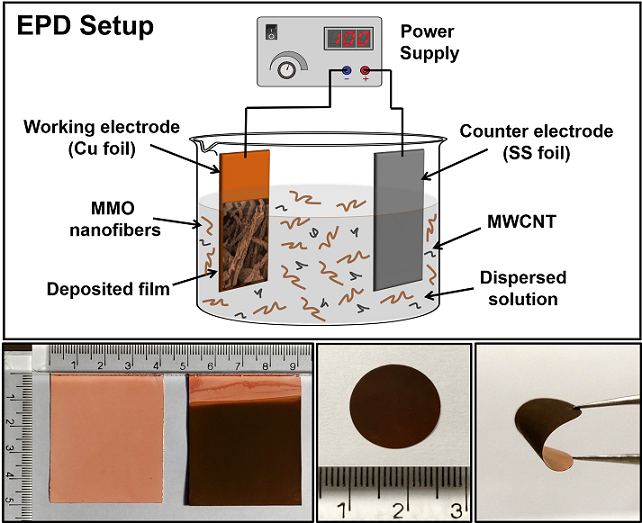
Recently, manganese (Mn)-based oxides have attracted more attention as a promising anode material for the next-generation lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) because of their higher experimental capacity, abundance, cost-effectiveness, and environmental- friendly nature. However, the poor rate capability and rapid capacity fading caused by the volume fluctuations during cycling hamper their usage in practical applications. To address these concerns, we report one-dimensional, high-aspect ratio MgMn2O4 (MMO) nanofibers with morphological voids/gaps as a binder-free negative electrode for LIBs. Herein, the binder-free electrodes of MMO nanofibers are fabricated via facile electrophoretic deposition technique. They can provide a well-designed network between the active materials and current collector, which enhances the electrical conductivity and Li-ion diffusion by avoiding binders as “dead mass”, which in turn helps to increase the energy density of LIBs. Furthermore, the morphological voids in between the individual nanoparticles of MMO nanofibers and the inactive MgO matrix element act as a buffering space that effectively accommodates the volume variation during lithiation and delithiation processes.